RecyclerView 指定 Item 滚动居中显示
这是一个老生常谈的话题了。
RecyclerView 提供了两个方法 scrollToPosition(position) 和 smoothScrollToPosition(position) 来将指定的 item 滚动到屏幕中,但不会居中显示,且在滚动到同一 position 的条件下,两个方法的最终效果也是不一样的(废话,方法名都不一样)。
其实我们距离成功只差半个屏幕了,与其从头开始实现,不如分析下上面两个方法,也许会带来事半功倍的效果。
1. scrollToPosition(position)
通过源码发现,在调用 recyclerView.scrollToPosition(position) 其实调用的是 layoutManager.scrollToPosition(position) 方法,下面是 LinearLayoutManager 对应的代码:
@Override
public void scrollToPosition(int position) {
//当 LayoutManager 需要滚动到某个位置时,设置 mPendingScrollPosition 为目标位置,进行重新布局时将检查此变量。
mPendingScrollPosition = position;
// 当调用 scrollToPositionWithOffset 方法时才使用到,这里不解释
mPendingScrollPositionOffset = INVALID_OFFSET;
if (mPendingSavedState != null) {
// 重置锚点
mPendingSavedState.invalidateAnchor();
}
// 请求重新布局
requestLayout();
}
顺藤摸瓜,接着调用 mRecyclerView.requestLayout(),触发 RecyclerView#onLayout 方法,在 onLayout 方法里调用 dispatchLayout() => dispatchLayoutStep2() 最后调用 mLayout.onLayoutChildren(mRecycler, mState),又回到了 LinearLayoutManager 里:
@Override
public void onLayoutChildren(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
// 布局算法主要分为 4 步:
// 1. 检查 Children 和其他变量,找到锚点信息,计算更新保存绘制锚点信息
// 2. 在锚点位置朝 start 方向上填充 ItemView
// 3. 在锚点位置朝 end 方向填充 ItemView
// 4. 滚动以满足从底部堆栈的要求。
...
if (!mAnchorInfo.mValid || mPendingScrollPosition != RecyclerView.NO_POSITION
|| mPendingSavedState != null) {
mAnchorInfo.reset(); // 锚点重置
mAnchorInfo.mLayoutFromEnd = mShouldReverseLayout ^ mStackFromEnd; // 布局方向,mStackFromEnd 默认为 false
// 重点来了:开始更新锚点信息!如果我们设置了有效的 mPendingScrollPosition
// 接下来将会在 updateAnchorFromPendingData(state, anchorInfo) 方法中将 anchorInfo.mPosition = mPendingScrollPosition;
// 这样就把锚点设置为了我们想要显示的目标位置了
updateAnchorInfoForLayout(recycler, state, mAnchorInfo);
mAnchorInfo.mValid = true;
}
...
// 后面就会按照锚点位置以及布局方向等信息开始布局绘制,以及各种滚动偏移量,这里不做过多的赘述
}
简单概括下 scrollToPosition(position) 的实现过程就是:把锚点设置为需要显示的目标位置,然后请求 RecyclerView 重新布局。这一过程看似简单,实则很复杂,且最终效果也不是我们想要的滚动居中的动态效果。
2. smoothScrollToPosition(position)
从名字就可以看出,这一过程是平滑的,还是接着扒源码,在调用 recyclerView.smoothScrollToPosition(position) 其实调用的是 layoutManager.smoothScrollToPosition(position) 方法,最终调用具体 LayoutManager 的 smoothScrollToPosition(RecyclerView recyclerView, State state, int position) 方法,下面是 LinearLayoutManager 对应的代码:
@Override
public void smoothScrollToPosition(RecyclerView recyclerView, RecyclerView.State state,
int position) {
// 创建一个线性平滑滚动器
LinearSmoothScroller linearSmoothScroller = new LinearSmoothScroller(recyclerView.getContext());
// 设置滚动器目标位置
linearSmoothScroller.setTargetPosition(position);
// 开始平滑滚动(如果目标位置不在屏幕范围内,则一直匀速滚动,一旦目标位置出现在屏幕上就减速滑动直至停止)
startSmoothScroll(linearSmoothScroller);
}
三行代码,简单粗暴,接下来分析下滚动器是如何发现目标位置的。先从 LinearSmoothScroller 的基类 SmoothScroller 入手:
2.1 SmoothScroller 是如何实现不断滚动的?
如果目标位置不在当前屏幕范围内,我们是无法获取到对应的 itemView 的,所以第一步就是让 RecyclerView 滚动起来。
调用 SmoothScroller#start 方法开始滚动,如下:
void start(RecyclerView recyclerView, LayoutManager layoutManager) {
...
// 开始滚动标记
mRunning = true;
...
//这里使用 ViewFlinger 进行滚动动画,ViewFlinger 实现了 Runnable 接口,并且内部使用了 OverScroller
mRecyclerView.mViewFlinger.postOnAnimation();
...
}
ViewFlinger 实现如下:
private class ViewFlinger implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
...
// 判断 scroller 滚动是否完成, true 为滚动未完成
if (scroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
...
//调用 SmoothScroller 的 onAnimation 方法,此方法将在下面详细分析
smoothScroller.onAnimation(dx - overscrollX, dy - overscrollY);
...
}
}
}
其实滚动的核心是不停地调用 ViewCompat.postOnAnimation(RecyclerView.this, action); 来实现动画效果。
2.2 SmoothScroller 是如何找到目标位置的?
还是以 LinearLayoutManager 为例,布局的核心流程都在 onLayoutChildren 方法里,一路追踪下去 onLayoutChildren => fill => layoutChunk => addDisappearingView => addViewInt => mSmoothScroller.onChildAttachedToWindow(child);
最终调用 SmoothScroller#onChildAttachedToWindow 方法如下:
protected void onChildAttachedToWindow(View child) {
// 每个 child 被“滚动”到屏幕上时都会调用该方法,判断下 child 的 position 是否等于目标位置即可
if (getChildPosition(child) == getTargetPosition()) {
// 找到我们要的 itemView 啦~
mTargetView = child;
...
}
}
前面提到过,在滚动的过程中,ViewFlinger 会不断调用 smoothScroller.onAnimation 方法,那么只要在这个方法里判断 mTargetView 是否为 null 就可以了:
private void onAnimation(int dx, int dy) {
...
if (mTargetView != null) {
// 再次核对下
if (getChildPosition(mTargetView) == mTargetPosition) {
// 最终回调 onTargetFound 方法
onTargetFound(mTargetView, recyclerView.mState, mRecyclingAction);
...
}
...
}
...
}
值得注意的是,当 onTargetFound 方法被调用时,mTargetView 并不一定被完整的显示出来,可能只"露出了一丢丢身子",也有可能已经完整出现在屏幕上了。
2.3 如何矫正目标 TargetView ?
onTargetFound 是抽象方法,来看下 LinearLayoutManager 具体是怎么实现 mTargetView 位置"矫正"的:
public class LinearSmoothScroller extends RecyclerView.SmoothScroller {
@Override
protected void onTargetFound(View targetView, RecyclerView.State state, Action action) {
// 计算矫正 targetView 需要再移动的水平距离
// getHorizontalSnapPreference() 此方法定义是否将 targetView 的左边缘或右边缘与父 RecyclerView 对齐。
final int dx = calculateDxToMakeVisible(targetView, getHorizontalSnapPreference());
// 计算矫正 targetView 需要再移动的垂直距离
// getVerticalSnapPreference() 此方法定义是否将 targetView 的上边缘或下边缘与父 RecyclerView 对齐。
final int dy = calculateDyToMakeVisible(targetView, getVerticalSnapPreference());
// 计算原始位置和最终位置的距离
final int distance = (int) Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
// 根据距离评估下动画时间
final int time = calculateTimeForDeceleration(distance);
if (time > 0) {
//向最终位置发起减速运动,最终让 targetView 矫正在指定位置
action.update(-dx, -dy, time, mDecelerateInterpolator);
}
}
···
}
其实到了这里,问题就变得很简单了,要实现“居中”效果,只要在 onTargetFound 方法里做文章就可以了,依葫芦画瓢。
3. 动手实现 scrollToCenter 效果
在此之前,不得不提下 RecyclerView 在 24.2.0 版本中新增的 SnapHelper 这个类,它用于辅助 RecyclerView 在滚动结束时将 Item 对齐到某个位置。由于是一个抽象类,官方又提供了一个 LinearSnapHelper 的子类,可以在 RecyclerView 滚动停止时将相应的 Item 停留中间位置,LinearSnapHelper 的效果已经非常接近我们的目标了,只不过 LinearSnapHelper 需要用户主动滑动,且仅仅是滚动停止时把距离中心最近的 Item 居中了。不过可以借鉴其实现思路结合 LinearSmoothScroller 实现我们的目标效果。
自定义 MyLinearSmoothScroller 实现自动滚动并居中的效果,完整代码如下:
class MyLinearSmoothScroller(context: Context) : LinearSmoothScroller(context) {
override fun onTargetFound(targetView: View, state: RecyclerView.State, action: Action) {
// 计算距离
val distance = distanceToCenter(
layoutManager!!,
targetView,
getOrientationHelper(layoutManager!!)!!
)
// 计算动画时间
val time = calculateTimeForDeceleration(distance)
if (time > 0) {
// 这里仅实现了水平或者垂直一种方向上的矫正,两者同时的情况暂不考虑
if (layoutManager!!.canScrollVertically())
action.update(0, distance, time, mDecelerateInterpolator)
else
action.update(distance, 0, time, mDecelerateInterpolator)
}
}
/**
* 计算 targetView 中心点到 RecyclerView 中心点的距离
*/
private fun distanceToCenter(
layoutManager: RecyclerView.LayoutManager,
targetView: View, helper: OrientationHelper
): Int {
val childCenter = helper.getDecoratedStart(targetView) + helper.getDecoratedMeasurement(targetView) / 2
val containerCenter = if (layoutManager.clipToPadding) {
helper.startAfterPadding + helper.totalSpace / 2
} else {
helper.end / 2
}
return childCenter - containerCenter
}
/**
* 不同方向上的距离使用不同的 OrientationHelper
*/
private fun getOrientationHelper(layoutManager: RecyclerView.LayoutManager): OrientationHelper? {
if (layoutManager.canScrollVertically()) {
return OrientationHelper.createVerticalHelper(layoutManager)
} else if (layoutManager.canScrollHorizontally()) {
return OrientationHelper.createHorizontalHelper(layoutManager)
}
return null
}
}
调用:
val scroller = MyLinearSmoothScroller(recyclerView.context)
//设置目标位置
scroller.targetPosition = 10
//开始平滑滚动
recyclerView.layoutManager!!.startSmoothScroll(scroller)
效果图如下:
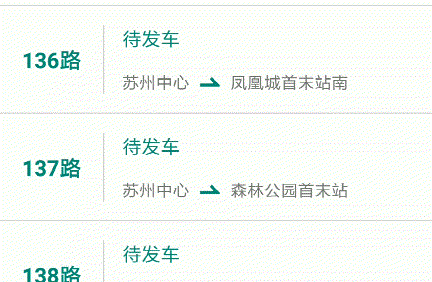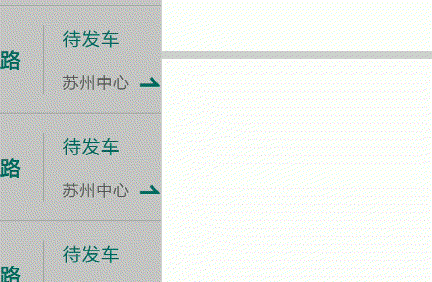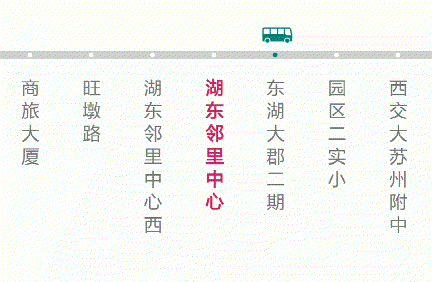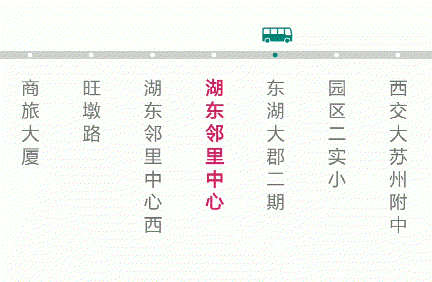
4. 总结
扒了一篇源码,果然受益匪浅